Could you pass a 2,000-year-old Chinese driving test?
In 2021, 10.8 million students took the college entrance exam (gaokao), but it wasn’t China’s biggest exam this year. That honor goes to the national driving test, which 13.9 million people passed this year, according to the Ministry of Public Security. As of September this year, over 410 million people in China have a driving license, while a mere 250 million have taken the gaokao since the exam was resumed in 1977 after the Cultural Revolution.
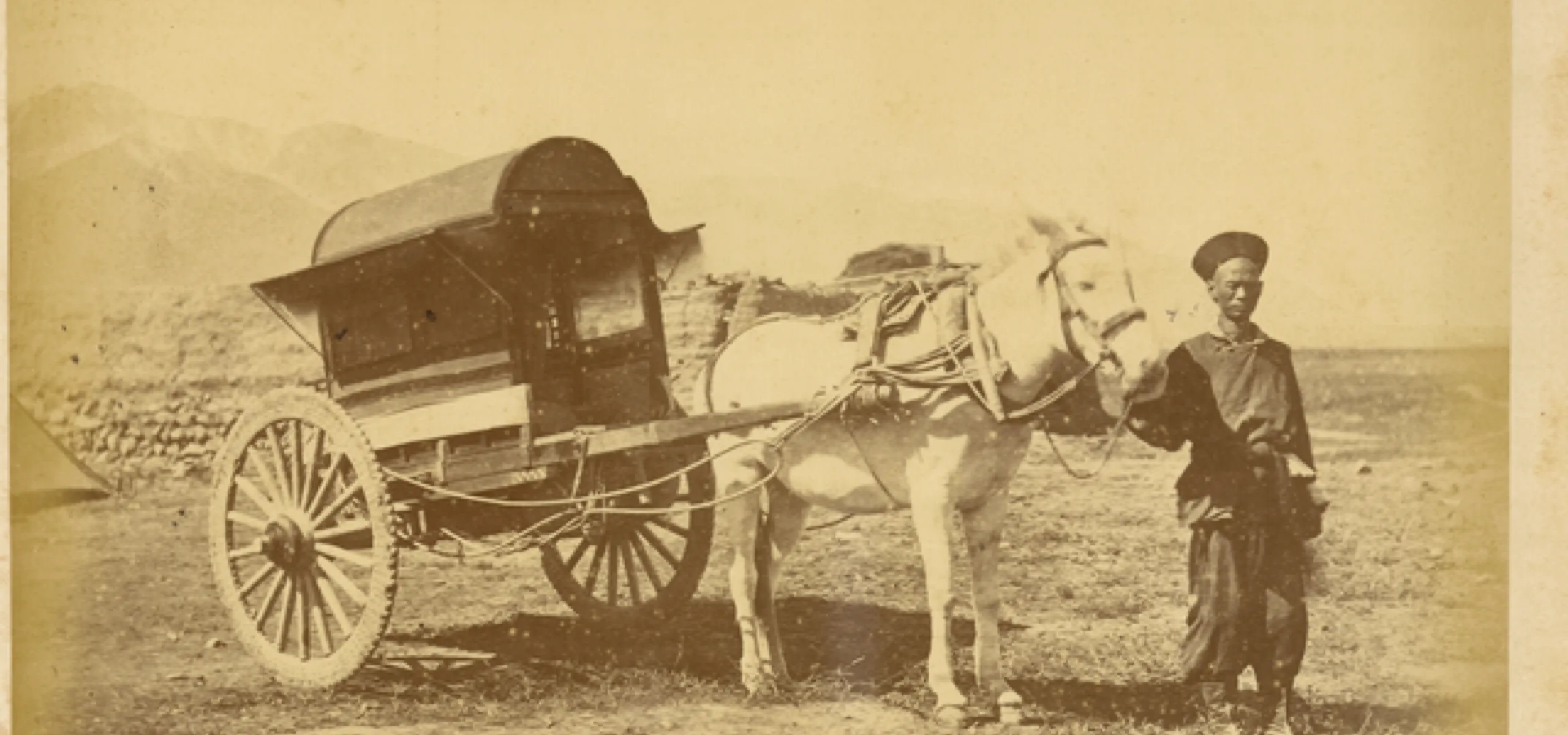
Obtaining a Chinese driver’s license involves four tests, two theoretical and two practical, and social media is awash with people complaining about how difficult it is to pass. But today’s tests are nothing compared with driving exams in centuries past, when drivers of horse-drawn carts had to moderate the movement of the carriage to make bells chime in a particular rhythm—and failing too many times could lead to punishment by forced labor.
Archaeological findings unearthed in Yinxu (in present-day Henan province) and oracle bone inscriptions show that in the Shang dynasty (1600 – 1046 BCE), horse-drawn chariots were already in use, especially for warfare. Later, in the Zhou dynasty (1046 – 256 BCE), these vehicles became used more widely for transport. According to the Rites of Zhou (《周礼》), a work on Zhou dynasty politics and culture, scholars of that time were required to learn charioteering as one of “six arts” which formed the basis of an education for a Confucian junzi (君子, noble man), along with rites, music, archery, calligraphy, and mathematics.
At that time, a qualified driver was called a “御人 (yùrén).” In order to become a yuren, one needed to pass a strict test that included five maneuvers, such as driving in foul weather and dodging obstacles on the road—techniques that certainly appear more difficult than today’s reverse parking and emergency stops.
Examinees would probably have been more nervous than today too. According to legal provisions written on bamboo slips unearthed in Hubei province in 1975, during the Qin dynasty (221 – 206 BCE), those who failed the test four times would be permanently deprived of their driving qualifications, and could face four years of forced labor as punishment.
But taking the test could be worth the risks. Excellent drivers were invaluable to the realm, as chariots were vital on the ancient Chinese battlefield. Horse-drawn carriages for warfare typically carried an archer, a lancer, and the driver, who was responsible for maneuvering the chariot into position for the soldiers to strike down the enemy.
Learning to drive could also improve one’s social standing. According to the Records of the Grand Historian (《史记》) by scholar Sima Qian (司马迁) of the Han dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE), there was a famous driver named Zaofu (造父) in the Zhou dynasty, who drove the carriage of King Mu of Zhou (周穆王). Once when King Mu was traveling in the west of his realm, the State of Xu rose in rebellion against him. With the kingdom under threat, Zaofu drove as fast as he could, apparently covering over 1,000 li (about 500 kilometers) in one day, allowing King Mu to return to the capital in time to organize the defense against the Xu rebels. Mu defeated the Xu army and rewarded Zaofu with lands in Zhao city (in the southwest of today’s Shanxi province), where Zaofu became a nobleman and adopted “Zhao” as his new surname.
Though Zaofu drove quickly during an emergency, most drivers still had to obey traffic laws. China’s earliest traffic regulations appeared in the Tang dynasty (618 – 907). According to the Laws of Tang Dynasty (《唐律疏议》), promulgated in 653, horse-drawn carriages were not permitted to “run” on the streets in the city except in emergencies, such as delivering urgent government documents or sending for a physician. Violators would be flogged 50 times as punishment, or convicted of a crime if death was resulted from their reckless driving. Drivers who caused injuries could be freed on bail, but should pay for the victim’s medical expenses, and could face other punishments depending on the condition of the injured person.